Which Curve in the Graph Best Represents a K-selected Species
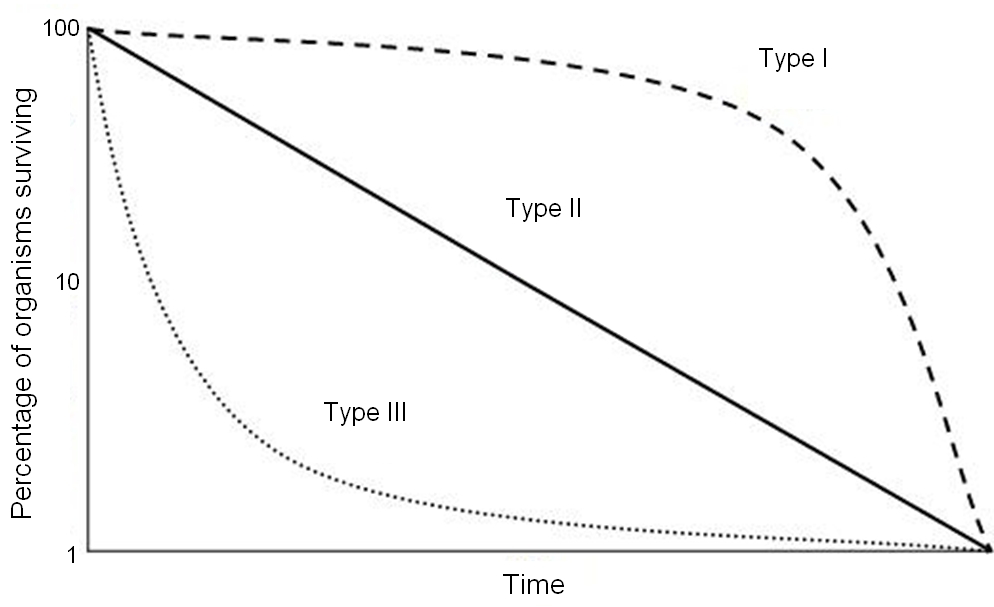
Survivorship curvesK-selected species usually have a Type I survivorship curve. Distribution of the population.

The Logistic Growth Model A Small Population Initially Experiences Exponential Growth As The Population Become Growth Biology Exponential High School Biology
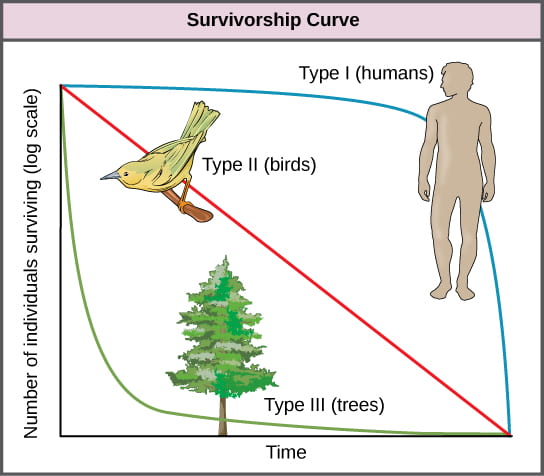
Type III or concave curves have the greatest mortality lowest age-specific survival early in life with relatively low rates of death high probability of survival for those surviving this bottleneck.

. Members of an r-selected species characteristically. Survivorship curve type 1. Are elephants K or R selected.
For making survivorship curves ecologists identify a cohort which is a group of individuals of the same species in the same population born at the same time. It can help us to know about various aspects such as life expectancy and age-specified survival of a particular species. Learn about r-selected vs.
Which of the following graphs best shows the population size of a K-selected species over time in a stable environment. It provides information regarding different population parameters like lifespan survival. Survivorship curves shows the decline of individuals with age.
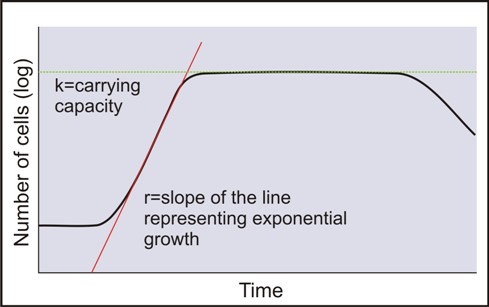
Notice that when N is almost zero the quantity in brackets is almost equal to 1 or KK and growth is close to exponentialWhen the population size is equal to the carrying capacity or N K the quantity in brackets is equal to zero and growth is equal to zeroA graph of this equation logistic growth yields the S-shaped curve bIt is a more realistic model of population growth. Distribution of traits across a population forms the natural selection. A constant probability of dying at any age shown by the Type II survivorship curve is evident as a straight line with a constant slope that.
Describe one evolutionary advantage and one disadvantage of being a specialist. This type of curve is characteristic of species that produce a large number of offspring see rK selection theory. This includes most marine invertebrates.
Elephants humans and bison are all k-selected species. This ScienceStruck article elaborates on the different survivorship curves with a few examples of each and also shows you how to create a survivorship curve on a spreadsheet in a stepwise manner. This type of survivorship curve is shown by typically K selected species.
Most plant species insect species frogs as well as marine species such as oysters and fishes have a Type III survivorship curve. The difference between an R-selected species and a K-selected species is that the R-selected species live in variable unstable habitats while K-selected species reside in stable environments. R-selected species produce many offspring but only a few live out their lifespan.
The world population growth rate in 2015 is about 1 percent. The middle graph. K-selected species because it has a low number of offspring per reproductive event.
Such species make up one of the two generalized life-history strategies posited by American ecologist Robert MacArthur and American biologist Edward O. The dashed line represents the carrying capacity of the species. K-selected species also called K-strategist species whose populations fluctuate at or near the carrying capacity K of the environment in which they reside.
A A B B C C D D. These species often have short life. A survivorship curve is a graph showing the number or proportion of individuals surviving to each age for a given species or group.
Which graph best illustrates a Type I Survivorship curve. This relatively flat curve reflects low juvenile mortality with most individuals living to old age. The following graph represents three survivorship curves Choose the description that best describes the graph a type I could represent the house mouse which is a typical r-selected species b type II could be the average of r-selected and K-selected species in a specific area c type III could represent elephants which are typical K-selected species.
Number of individuals in the species. Which curve in the graph best represents a KK-selected species. K-selected species have a few offspring that have a long life expectancy.
In a K-selected species graph the line where the graph levels off is the. On the other hand r-selected species often inhabit unstable environments and are completely density independent. In the type I curve the mortality rate at juvenile newborn is comparatively low as maximum deaths occur at the post-reproductive phase.
Discover examples of rK strategies and examine how to graph the growth of r-selected and K-selected species. Which of the following would best represent a clumoed population distribution pattern. K-selected species B r-selected species C Type I survivorship D Type II survivorship.
K- selected species are more likely to have a stable population curve and be a specialist and r-selected species are more likely to have an irruptive curve and be a generalist. R-selected speciesthat is species whose populations. It is expected to drop to 05.
K represents the carrying capacity r represents the population growth rate and selected refers to traits employed by the organism to optimize either the carrying capacity or population growth rate. The black rhino is a K. It can be depicted in a graph.
The carrying capacity of an environment for a particular species at a particular time is determined by the. These are directional selection disruptive selection and stabilizing selection. There is three types of natural selections.
D increasing numbers of women entering the workforce in developing nations. However the students should be able to identify definitively that the red-tailed hawk is more K-selected than the roadrunner the Western rattlesnake is more K-selected than the Whiptail lizard and that the coyote is more K-selected than the Kangaroo mouse. II survivorship curve as shown in the graph.
Possesses various r- and K-selected characteristics but must be considered as a whole. Reach sexual maturity quickly. Because they become older and more susceptible to diseases and predation.

Difference Between R And K Selection In Ecology Biology Notes Learning Resources Biology
A Simple Method For Estimating The Lorenz Curve Humanities And Social Sciences Communications
Population Ecology 1 Biological Principles

3 Types Of Survivorship Curves Dfeinition Keystone Species Biology Notes Ecology

Population Ecology Life Tables And The Rate Of Population Growth Britannica

R Selected Vs K Selected Species Overview Population Growth Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
K And R Reproductive Strategies

Survivorship Curves Ap Environmental Science Biology Units Science Topics

Population Ecology Logistic Population Growth Britannica

4 2 Population Growth And Regulation Environmental Biology

Carrying Capacity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

R Selected Vs K Selected Species Overview Population Growth Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Comments
Post a Comment